GENSCAT Generate a distribution of scatterers
GENSCAT generates a 2-D or 3-D distribution of scatterers.
Contents
Syntax
[XS,YS,ZS] = genscat([WIDTH HEIGHT],MEANDIST) generates a 2-D pseudorandom distribution of scatterers such that the mean distance between a scatterer and its nearest neighbor is approximately MEANDIST. The vector [WIDTH HEIGHT] (unit = m) specifies the width and height of the rectangular ROI to which the scatterers belong. The middle of its lower edge (in the x-z coordinate system) is located at (0,0). In this 2-D syntax, YS is a vector of zeros.
[XS,YS,ZS] = genscat([WIDTH HEIGHT DEPTH],MEANDIST) generates a 3-D pseudorandom distribution of scatterers such that the mean distance between a scatterer and its nearest neighbor is approximately MEANDIST. The vector [WIDTH HEIGHT DEPTH] (unit = m) specifies the width (x-direction), height (z-direction), and depth (y-direction) of the ROI box to which the scatterers belong. The center of its lower face (in the x-y-z coordinate system) is located at (0,0,0).
[XS,YS,ZS,RC] = genscat([...],MEANDIST,I) also returns the reflection coefficients RC of the scatterers. The RC values follow Rayleigh distributions whose means are calculated from the image I. I must be a 2-D or 3-D image whose size is given by [WIDTH HEIGHT] (2-D) or [WIDTH HEIGHT DEPTH] (3-D).
If a 2-D image I is given as an input, you can use [WIDTH NaN] or [Nan HEIGHT]. The missing value is calculated from the pixel-based size of the image I while preserving the aspect ratio. Similarly, [WIDTH Nan NaN], [Nan HEIGHT NaN], or [NaN NaN DEPTH] can be used with a 3-D image. If I is empty or omitted, then I is assumed to be an image of ones.
[...] = GENSCAT(...,G) assumes that the dynamic range of the input image I is G dB (defaut value = 40 dB). If G<=1, it is assumed that the image I is gamma-compressed, with gamma = G.
A note on MEANDIST
We recommend a MEANDIST value less than or equal to the minimum wavelength (at -6 dB). For a speed of sound c, from the PARAM structure generated by GETPARAM, you may use
MEANDIST = PARAM.c/(PARAM.fc*(1+PARAM.bandwidth/200)),
or a smaller value. This value is used automatically if you input the PARAM structure instead of MEANDIST:
[...] = genscat([...],PARAM,I)
By default, PARAM.c = 1540 [m/s] and PARAM.bandwidth = 75 [%], as in PFIELD.
Example: Cardiac scatterers
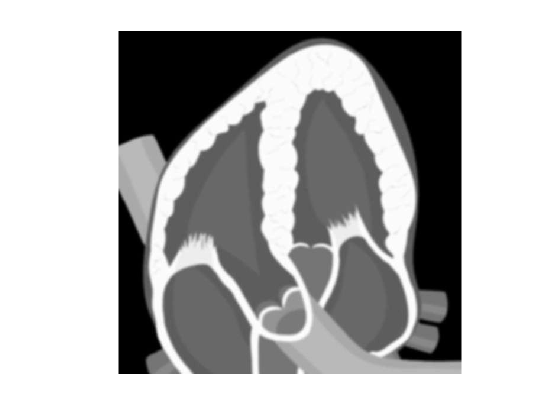
This example shows how to generate a 2-D distribution of scatterers from a simplified image of the heart.
Read the heart image and make it gray
I = imread('heart.jpg'); I = rgb2gray(I); [nl,nc] = size(I); imshow(I,'InitialMagnification','fit')
Choose a cardiac phased array
param = getparam('P4-2v');
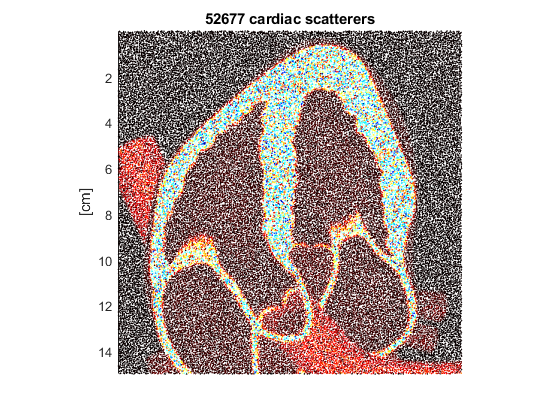
Create a 2-D distribution of scatterers whose depth is 15 cm. RC will contain the reflection coefficients.
[xs,~,zs,RC] = genscat([NaN 15e-2],param,I);
Display the scatterers
scatter(xs*1e2,zs*1e2,2,RC,'filled') colormap([hot; 1-hot]) axis equal ij tight set(gca,'XColor','none','box','off') title([int2str(numel(RC)) ' cardiac scatterers']) ylabel('[cm]')
See also
simus, simus3, rmscat, getparam
About the author
Damien Garcia, Eng., Ph.D. INSERM researcher Creatis, University of Lyon, France
websites: BioméCardio, MUST
Date modified